Axcess FX would like to welcome you to our forex trading roadmap.
Our forex roadmap informs you of all the areas you will need to understand as part of the journey to transform from a novice to an expert forex trader. You must be well prepared to face any challenges and successfully seize trading opportunities the forex market presents.

Ultimately you need to maximize your potential for success in this competitive and dynamic trading environment.
In this roadmap, we will cover various topics under seven main sections. It will include the fundamentals of forex trading, trading strategies and systems, risk management and trading psychology, technical and fundamental analysis, and the importance of ongoing education and self-improvement.
Prepare to embark on an exciting and rewarding journey as we outline the critical areas needed to progress from a beginner toward forex trading mastery!
Table Of Contents
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| I. The Fundamentals of Forex Trading | An introduction to the basic concepts and principles of forex trading, including currency pairs, market participants, and key terms. |
| II. Trading Strategies and Systems | A presentation of various trading strategies and tips on developing a personalized trading system through backtesting and refinement. |
| III. Risk Management and Trading Psychology | Examining the importance of risk management, position sizing, and overcoming psychological challenges in forex trading. |
| IV. Technical Analysis | An exploration of technical analysis tools and techniques, including chart types, support and resistance levels, and technical indicators. |
| V. Fundamental Analysis | A discussion of how economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events impact forex markets and currency exchange rates. |
| VI. Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis | An explanation of the benefits of using both technical and fundamental analysis and strategies for incorporating them in a trading system. |
| VII. Continuing Your Forex Trading Journey | Emphasizing the importance of ongoing education, learning from mistakes and successes, and seeking mentorship for growth and improvement. |
| VIII. Conclusion | A summary of the key takeaways from the Forex Trading Roadmap, encouraging readers to continue learning and growing as traders. |
I. The Fundamentals of Forex Trading
In this first section, we look at the most fundamental concepts of FX trading; it importantly includes currency pairs, the basics of the market, roles played by various market participants, and all the jargon that every trader must know to be able to trade proficiently.
What is a Currency Pair?
In the forex market, currencies trade in pairs, meaning you simultaneously buy one currency while selling another. The primary reason for this is that exchange rates are always quoted in pairs, reflecting the relative value of one currency against another. For example, the EUR/USD currency pair is the exchange rate between Euros and US Dollars. If you believe the Euro will appreciate against the US Dollar, you will buy the EUR/USD pair when trading this pair. Conversely, you will sell the pair if you think the Euro will depreciate.

Currency pairs generally divide into three categories which are as follows:
Major pairs
These are the most liquid and widely traded currency pairs, comprising the US Dollar and one of the seven other major currencies (GBP, EUR, JPY, CAD, CHF, NZD, AUD). Examples include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD.
Minor pairs
Also known as cross-currency pairs, these do not involve the US Dollar. Examples include EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY, and GBP/JPY.
Exotic pairs
Exotic currency pairs involve currencies from smaller economies or emerging markets. They are much less liquid and more volatile than major and minor pairs. Examples include USD/RON (US Dollar/Romanian Leu) and EUR/NOK (Euro/Norwegian Krona).
Understanding the Forex Market
The forex market is a fully decentralized and Over The Counter (OTC) market where the participants trade currencies directly. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with trading centers in major financial hubs such as London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. The FX market is the largest, most liquid financial market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion.
The Different Types of Market Participants and Their Roles
The forex market comprises various participants, each with different roles and objectives. Some of the key players are represented in the table below:
Different Types of Market Participants and Their Roles
| Market Participant | Role |
|---|---|
| Central banks | Manage a country’s monetary policy and intervene in the forex market to influence exchange rates and maintain economic stability. |
| Commercial banks | These institutions facilitate forex transactions for their clients and use proprietary trading to profit from exchange rate fluctuations. |
| Hedge funds and institutional investors | These participants trade currencies as part of their investment strategies, often taking prominent positions to capitalize on short-term market movements. |
| Corporations | Businesses engaged in international trade need to exchange currencies for transactions or hedge against currency risk. |
| Retail traders | Individual investors like you and me trade forex through online platforms and brokers, seeking to profit from exchange rate fluctuations. |
The Key Terms and Concepts in Forex Trading
To trade proficiently, you must understand what the following terms mean:
- Bid + Ask Price: The bid is the highest acceptable price a buyer will pay for a currency pair, while the ask is the lowest price a seller will accept. The difference between the bid and the ask price is called the spread, which represents the transaction cost for traders.
- Leverage: Leverage enables traders to control more significant positions with less capital. For example, with a 50:1 leverage, a trader can hold a $50,000 position with just $1,000 in their account. However, leverage also magnifies potential losses, so it’s essential to use it judiciously.
- Margin: Margin is the amount of money a forex trader needs to deposit in a trading account to open and keep a leveraged position. It serves as collateral for the borrowed funds used in leveraged trading.
- Pip: A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement in the forex market, typically equal to 0.0001 for most currency pairs. For example, if the EUR/USD moves from 1.1200 to 1.1201, it has moved by one pip. Some brokers also quote prices to a fraction of a pip, known as pipettes, providing more precise pricing.
- Lot Size: A lot is the standard unit size of a forex trade. 100,000 units of the base currency represent a standard lot, while mini, micro, and nano lots represent 10,000, 1,000, and 100 units, respectively. Lot sizes help traders control risk and customize their trading positions based on their account size and risk tolerance.
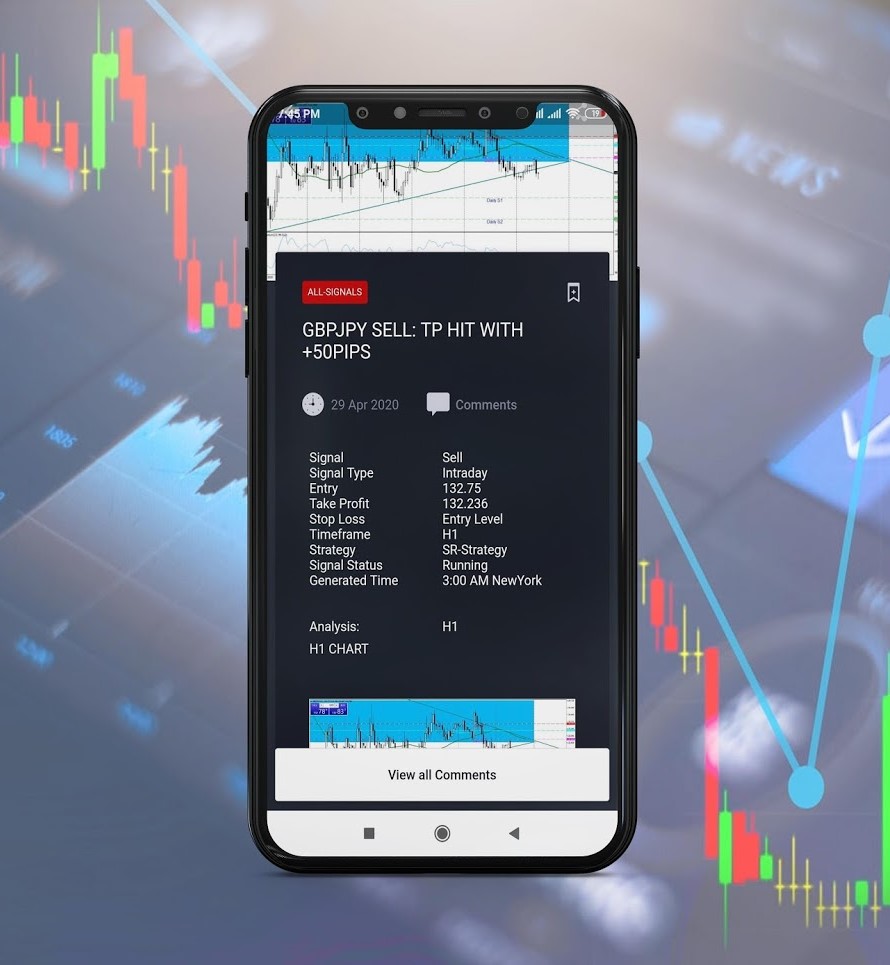
II. Trading Strategies and Systems
As part of the journey to become a successful forex trader, it is vital to understand the concept of different forex trading strategies, how to develop a bespoke trading system catering to your needs, and how to backtest a system.
An Overview of Various Trading Strategies
There are many complex strategies, but when starting, you need to be aware at a minimum of the following basic concepts.
Trend-following strategies
Trend-following strategies aim to capitalize on an existing market trend by entering trades in the direction of the trend. These strategies are based on the assumption that a trend will continue and can be applied in both long-term and short-term trading. Some popular trend-following indicators include moving averages, the MACD, and the ADX.
Range-bound strategies
Range-bound strategies employ when the market moves within a defined horizontal price range with no clear upward or downward trend. Traders using this approach look to buy at support levels and sell at resistance levels, taking advantage of the price oscillations. Standard tools for identifying support and resistance levels include horizontal trend lines, pivot points, and Fibonacci retracements.
Breakout strategies
Breakout strategies focus on identifying and trading breakouts, which occur when the price moves beyond a specific support or resistance level with increased volume. Breakout traders aim to enter a trade as the price breaks through the level, anticipating that the breakout will lead to a significant price movement in that direction. Chart patterns like triangles, rectangles, and head and shoulders can help identify potential breakouts.
Developing a Trading System
Once you have decided upon the strategy that may suit your personality or trading style, you must develop a trading system to implement that strategy efficiently.

Choosing a suitable time frame
An appropriate time frame is crucial for developing a trading system that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. Short-term traders, such as scalpers and day traders, often use shorter time frames (e.g., 1-minute, 5-minute, or 15-minute charts), while swing traders and position traders may opt for longer time frames (e.g., 4-hour, daily, or weekly charts).
Identifying entry and exit signals
Your trading system should include straightforward entry and exit signals based on technical or fundamental analysis. It may involve using a combination of indicators, chart patterns, or economic data releases to generate trading signals.
Backtesting and refining the system
Backtesting involves testing your trading system on historical price data to evaluate its performance and identify weaknesses. Once you’ve backtested your system, you can refine it by adjusting parameters or incorporating additional indicators to improve performance.
Automated Forex trading software
As you become more experienced, you may want to consider automated forex trading software as an accompaniment to any trading strategy and trading system. We have a dedicated guides on automated trading software including top forex robots.
III. Risk Management and Trading Psychology
In this section, we will cover an often overlooked part of what it takes to become an experienced trader: risk management and trading psychology.
The Importance of Risk Management in Forex
Risk management is a vital part of forex trading that ensures your exposure to losses is controlled, and your trading account remains protected. Effective risk management involves:
- Setting appropriate stop-loss orders.
- Managing position sizes.
- Maintaining a favorable risk-reward ratio.
By managing risks effectively, traders can mitigate potential losses and improve the longevity of their trading careers.
Position Sizing and Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Position sizing is about deciding the appropriate trade size based on your account balance and risk tolerance. Proper position sizing ensures you are not overexposing your account to risk and can withstand potential losses without jeopardizing your trading account. A standard position sizing method is the percentage risk rule, where traders risk a fixed percentage of their account balance on each trade.
Stop-loss orders are a vital risk management tool that allows traders to predefine the maximum loss they are willing to accept on a trade. By setting stop-loss orders, traders can limit their losses and protect their trading capital. A well-placed stop-loss order considers the market’s volatility, the trader’s risk tolerance, and the technical support and resistance levels.

The Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio compares the potential profit of a trade to the possible loss. A favorable risk-reward ratio ensures that potential gains outweigh potential losses over time, allowing traders to maintain a profitable forex trading account even if they experience a few losses. A standard guideline aims for a minimum risk-reward ratio of 1:2 or higher, meaning the potential profit should be at least twice the possible loss.
How to Overcome Psychological Challenges in Trading
Forex trading is psychologically challenging, and it is vital to overcome these challenges in the journey toward successful trading.
Dealing with emotions like fear and greed
Both fear and greed are powerful emotions that can negatively impact trading decisions, leading to impulsive actions or hesitation. To manage these emotions, traders should develop a clear trading plan, adhere to their risk management rules, and practice mindfulness techniques. By maintaining a rational approach to trading, traders can minimize the influence of fear and greed on their decisions.
Developing a disciplined trading mindset
A disciplined trading mindset means consistently following your trading plan, adhering to risk management rules, and avoiding spur-of-the-moment decisions. Cultivating discipline requires setting realistic goals, maintaining a trading journal to track performance and progress, and continually reviewing and analyzing trading performance. A disciplined mindset enables forex traders to stay focused on their trading strategy and make rational decisions, even during intense market volatility.
IV. Technical Analysis
Forex technical analysis is the study of historical price data and chart patterns to predict future market movements and identify potential trading opportunities.
Understanding Chart Types and Timeframes
There are three primary chart types used to trade forex. These are line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts. Line charts are the simplest, connecting the closing prices of each period. Bar charts display each period’s open, high, low, and close prices. In contrast, candlestick charts provide the same information but with a more visual representation, using colored “candles” to depict price movement.
Timeframes refer to the period that each data point on a chart represents. Traders can choose from various timeframes, ranging from 1-minute charts to monthly charts. The choice of timeframe depends on the trader’s style, risk tolerance, and trading goals. Short-term traders typically use shorter timeframes, while long-term traders focus on longer timeframes.
Identifying Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance are critical price levels where buying and selling pressure tends to shift. Support levels represent areas where the price has found a “floor,” while resistance levels indicate areas where the price has found a “ceiling.” Identifying these levels can help traders determine potential entry and exit points and set stop-loss orders. Standard methods for identifying support and resistance levels include horizontal trend lines, pivot points, and Fibonacci retracements.
Trend Lines and Moving Averages
Trend lines are diagonal lines drawn on a price chart to connect successive highs or lows, indicating the direction of the market trend. Upward-sloping trend lines connect higher lows, representing an uptrend, while downward-sloping trend lines connect lower highs, signifying a downtrend. Traders can use trend lines to identify potential trade entry points, set stop-loss orders, and gauge the trend’s strength.
Moving averages are widely used indicators that smooth out price data, helping traders identify trends and potential reversals. There are two critical moving averages: simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA). SMAs calculate the average price over a specified period, while EMAs give more weight to recent price data. Forex traders often use multiple moving averages with different timeframes to generate trading signals and confirm trends.
Technical Indicators and Oscillators
Technical indicators and oscillators are mathematical tools that analyze price data to generate trading signals and gauge market conditions. Some popular technical indicators include Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands. Oscillators, such as the Stochastic Oscillator and the Commodity Channel Index (CCI), help traders identify overbought and oversold conditions, signaling potential reversals.
Candlestick Patterns and Chart Patterns
Candlestick patterns are specific formations on candlestick charts that provide insights into market sentiment and potential price movement. Some common candlestick patterns include the doji, hammer, shooting star, and engulfing patterns. By recognizing these patterns, traders can anticipate possible trend reversals or trend continuations, leading to more informed trading decisions.
Chart patterns are geometric formations on price charts that indicate potential market movements. They can be classified into two categories: continuation patterns and reversal patterns. Continuation patterns like triangles and flags suggest the trend will likely continue. Reversal patterns, such as head and shoulders and double tops/bottoms, indicate a potential market change. By recognizing these chart patterns, traders can make more informed decisions about entry and exit points and better anticipate likely market movements.
V. Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis in forex evaluates economic, political, and social factors to assess a currency’s true value and predict its future performance in the market.
Understanding the Impact of Key Economic Indicators on Forex Markets
Economic indicators are statistical data reflecting a country’s economic health, which can significantly impact currency exchange rates. Some of the most influential economic indicators are included in the table below:
Most Influential Economic Indicators
| Economic Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | A measure of a country’s overall economic output, GDP growth can affect currency strength. Higher GDP growth generally indicates a robust economy, attracting foreign investment and boosting the domestic currency. |
| Employment Data | Indicators such as the unemployment rate and non-farm payrolls provide insights into the labor market’s health, with robust employment data typically supporting a country’s currency. |
| Inflation | Central banks monitor inflation rates closely to maintain price stability. High inflation can lead to currency depreciation, while low inflation may prompt central banks to stimulate the economy, impacting currency values. |
| Interest Rates | Central banks set interest rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. Higher interest rates often lead to currency appreciation as they attract foreign capital, while lower rates can weaken a currency. |
Effects of Central Bank Monetary Policies on Currencies
Central banks play a significant role in currency values through their monetary policies, including setting interest rates, implementing quantitative easing, and intervening in the forex market. These actions can directly impact currency exchange rates by influencing inflation, economic growth, and investor sentiment.
For example, when a central bank raises interest rates, it often leads to currency appreciation, as higher interest rates attract foreign capital. Conversely, lowering interest rates or implementing quantitative easing can lead to currency depreciation, as these actions can increase the money supply and stimulate inflation.
Geopolitical Events and Their Influence on Currency Exchange Rates
Geopolitical events, such as elections, political tensions, wars, and trade disputes, can substantially impact currency values. These events can cause economic uncertainty, affecting investor sentiment and risk appetite.
For instance, political instability or conflict in a country can lead to decreased investor confidence, resulting in capital outflows and currency depreciation. Conversely, resolving a trade dispute or a favorable election outcome may boost investor confidence, leading to currency appreciation.
How to Use Economic Calendars in Forex Trading
Economic calendars are essential for forex traders, providing a schedule of upcoming economic events and data releases. By staying informed about these events, traders can better anticipate potential market movements and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
To effectively use an economic calendar, adhere to the following steps:
Step 1: Familiarize yourself with the most relevant economic indicators for the currencies you trade, as not all indicators impact each currency equally.
Step 2: Monitor upcoming data releases and events, noting their expected impact on currency values based on historical trends and market expectations.
Step 3: Plan your trading activities around these events, considering potential market volatility and adjusting your risk management strategies accordingly.
Step 4: Please keep track of actual data releases and compare them to market expectations, as discrepancies between the two can lead to significant market movements.
VI. Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Using both technical and fundamental analysis as part of a wider forex trading strategy has many benefits.
Comprehensive market analysis
Combining technical and fundamental analysis allows traders to analyze the forex market from multiple perspectives, leading to a more accurate understanding of market dynamics. Technical analysis focuses on price movements and trends, while fundamental analysis evaluates the underlying economic factors driving currency values. By using both methods, traders can make more informed decisions based on a complete market picture.

Improved trade timing
Technical analysis can help traders identify optimal trade entry and exit points based on price patterns and trends. In contrast, fundamental analysis can provide a broader context for these decisions by highlighting the economic factors likely to impact currency values. Combining these approaches can help traders refine their trade timing, potentially improving overall trading performance.
Adaptability
Markets are constantly changing, and a trading strategy that relies solely on technical or fundamental analysis may struggle to adapt to evolving conditions. By incorporating both methods, traders can develop a more flexible and adaptable trading strategy to navigate better shifting market dynamics.
Risk management
A well-rounded trading strategy incorporating technical and fundamental analysis can help traders manage risk more effectively. By understanding both the technical and fundamental aspects of the market, traders can make better-informed decisions about position sizing, stop-loss orders, and risk-reward ratios.
Following best practice will allow for the incorporating of both techniques in your trading system.
Develop a trading plan
A solid trading plan should outline your preferred trading strategies, risk management principles, and the role of both technical and fundamental analysis in your decision-making process. Establish guidelines for when and how you will use each type of analysis and how they will work together to inform your trading decisions.
Combine trade signals
Utilize technical and fundamental analysis to generate trade signals. For example, you might use technical analysis to identify potential entry points based on support and resistance levels or chart patterns while considering the broader economic context of fundamental analysis. By confirming trade signals with both methods, you can increase your confidence in trading decisions and improve your overall trading performance.
Stay informed
Keep up-to-date with economic news, data releases, and market analysis to inform your fundamental analysis. Additionally, maintain your technical analysis skills by regularly reviewing charts and familiarizing yourself with new technical indicators and tools. Staying informed about both market aspects can help you make more accurate predictions and adjust your trading strategies as needed.
Regularly review and adjust
Continuously assess the effectiveness of your trading strategy and make adjustments as needed. Monitor your trading performance and consider whether your technical and fundamental analysis approach effectively governs your trading decisions. Be open to refining your strategy and incorporating new techniques or tools as you learn and grow as a trader.
VII. Continuing Your Forex Trading Journey
The final section of our roadmap is how to continue progressively on your forex trading journey and consists of four key areas.
The Importance of Ongoing Education and Self-Improvement
- Staying competitive: The forex market is highly competitive, with traders from around the world vying for profits. Staying focused in forex trading by continuously improving your knowledge, skills, and trading strategies is important to stay ahead of the curve. It includes keeping up with market news, economic developments, and new trading tools and techniques.
- Adapting to market changes: The forex market is dynamic and ever-changing. As a trader, you must adapt to these changes by updating your strategies and staying informed about new trends, economic events, and market conditions. Continuous learning allows you to remain agile and responsive in evolving market dynamics.
Learning from Trading Mistakes and Successes
- Identifying areas for improvement: Reflecting on your trading mistakes can provide valuable insights into areas where you can improve. By analyzing what went wrong, you can identify weaknesses in your trading strategy, risk management, or execution and take steps to address them.
- Building on successes: Analyzing your successful trades can help you understand what works well and why. By focusing on the elements that contributed to your success, you can refine and enhance your trading strategy to achieve even better results in the future.
Keeping a Trading Journal for Reflection and Growth
- Recording trade details: A trading journal is a valuable tool for tracking your trades, including entry and exit points, position sizes, and the rationale behind each decision. By keeping a detailed record of your trades, you can more easily identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
- Reviewing and reflecting: Regularly reviewing your trading journal allows you to reflect on your performance, learn from your mistakes and successes, and make informed decisions about improving your trading approach. This self-assessment and reflection process is crucial for a trader’s growth and development.
Seeking Mentorship and Learning from Other Successful Traders
- Gaining valuable insights: Learning from experienced traders can provide invaluable insights into successful trading strategies, risk management techniques, and the psychological aspects of trading. By seeking mentorship or participating in trading communities, you can access a wealth of knowledge and experience to help you improve as a trader.
- Networking and support: Connecting with other traders can also provide a valuable support network, helping you stay motivated and focused on your trading journey. Sharing experiences, successes, and challenges with like-minded individuals can be both inspiring and encouraging, helping you stay committed to your growth and development as a trader.
VIII. Conclusion
A well-rounded forex education is crucial for success. It equips you with the tools and knowledge needed to make informed trading decisions, from understanding the forex market fundamentals and mastering various trading strategies to employing effective risk management and trading psychology techniques.
Continuing your forex trading journey through ongoing education, self-improvement, and learning from mistakes and successes is vital in staying competitive and adaptive in the ever-evolving forex market.
Embarking on your path to becoming a successful forex trader requires persistence, dedication, and a growth mindset. You will need to embrace challenges, seek mentorship from seasoned traders, and always strive to grow and improve. By following this roadmap and maintaining your commitment to growing, you will be well on your way to a successful forex trading career.
Written by Chris Gillie

Chris Gillie is the founder of Axcess FX, a forex software review and research website. He is a former investment banker who worked in FX Sales on the UBS London trading floor. Chris has been using forex trading software as part of his trading set-up since the late 2000s and the embryonic days of MetaTrader and the MQL coding language.
